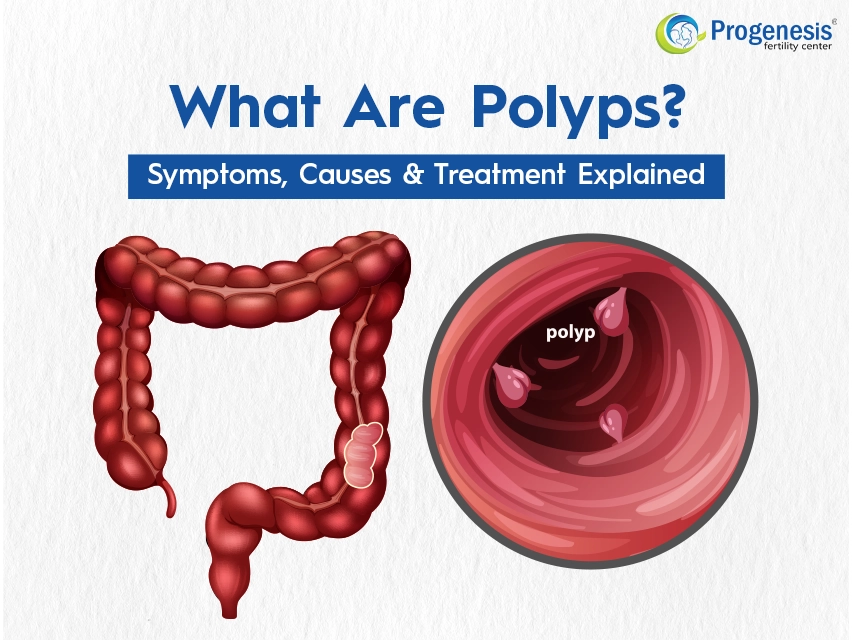
What Are Polyps?
Polyps are growths that can form in numerous regions of the body, most notably the colon, uterus, stomach, and nose. While many polyps are benign (non-cancerous), some can become cancerous, particularly if they are of a specific type, like adenomatous polyps.
Types & Symptoms of Polyps

Colorectal polyps: Can cause changes in bowel movements (constipation or diarrhea), blood in the stool or rectal bleeding, abdominal pain, and iron deficiency anemia.
Nasal polyps: Can cause nasal congestion, a runny nose, headaches, loss of smell and taste, and postnasal drip.
Cervical polyps: Can cause abnormal vaginal bleeding, discharge, or bleeding after sexual intercourse, however they rarely cause any symptoms.
Uterine polyps: Can result in irregular menstrual flow, heavy periods, or bleeding beyond menopause.
Stomach polyps: Can cause pain, nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Ear canal polyps: Can cause hearing loss, discharge from the ear, and pain.
Causes of Polyps
Here are some of the causes of polyps-
Abnormal cell growth: Polyps typically result from abnormal cell development in the affected area's lining.
Chronic inflammation: Chronic inflammation, such as chronic sinusitis, could lead to the formation of nasal polyps.
Genetics: Certain polyps, such as those linked to familial adenomatous polyposis, can be inherited.
Other factors: Other factors that can contribute to the development of polyps include illegal substances (e.g., proton pump inhibitors), bacterial infections (e.g., H. pylori), and age.
Also Read: What is Bulky Uterus? its Symptoms, Causes and Treatments
Diagnosis of Polyps
Polyps can be diagnosed using a variety of procedures based on their location, including:
Colonoscopy: Colonoscopy is the most reliable method for diagnosing colon polyps. It enables both direct viewing and elimination of polyps throughout the colon.
Upper Endoscopy: Upper endoscopy is performed to identify stomach polyps. This treatment includes putting a flexible tube with a camera down the mouth to inspect the upper digestive tract.
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy: Flexible sigmoidoscopy is a way of finding polyps in the very last part of the colon.
Virtual colonoscopy (CT colonography): It uses CT scans to create pictures of the colon and rectum. It is a non-invasive method of detecting colon polyps, but any abnormalities seen must be followed up with a regular colonoscopy.
Also Read: Guide to Female Infertility: Symptoms, causes & Treatment
Treatment Options for Polyps
Some of the treatment options for polyps include:
Medication: Medications such as corticosteroids (nasal sprays or pills) can be used to treat nasal polyps.
Surgery: In certain situations, surgery may be required to remove polyps, especially if they are large or causing symptoms.
Biopsy: A biopsy is commonly used to identify the type of polyp and if it is cancerous.
Active surveillance: When polyps are small and benign, doctors may propose monitoring them rather than removing them right away.
Lifestyle changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity, eliminating smoking and alcohol, and maintaining a healthy weight, can lower the chance of colon polyps.
Also Read: Does Alcohol and Smoking Harm Men's Fertility & Sex Life?
Prevention and Risk Factors
To lower the risk of getting polyps, one can take the following preventive measures:
Healthy diet: A healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while restricting processed foods and red meat, can lower the risk of developing polyps.
Physical activity: Regular exercise improves general health and reduces the risk of polyps.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can help lower the risk.
Avoiding smoking and alcohol: Avoiding smoking and alcohol can improve general health and lower the chance of polyps.
Regular screening: Regular colonoscopies assist in finding and removing polyps before they become malignant.
Also Read: How to get pregnant after 40?
Risk Factors:
Here are some of the risk factors that can cause polyps:
Age: The chance of getting colon polyps rises with age, especially beyond 50.
Family History: A history of polyps or colon cancer raises the risk.
Genetics: Certain hereditary disorders may predispose people to polyps.
Lifestyle: Smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, obesity, and a diet rich in red meat and processed foods all enhance the risk.
Other conditions: Diabetes, chronic inflammatory bowel illness, and certain autoimmune conditions can all raise the risk.
Also Read: What are the different types of infertility treatments?
Conclusion
Discovering or hearing about polyps can be alarming, but keep in mind that the majority of polyps are harmless and easily curable if identified early. Modern diagnostic techniques and routine screenings allow doctors to detect and manage polyps before they become a major problem. Staying informed, getting regular checkups, and following medical recommendations can help you keep your health and peace of mind. If you have any questions or conces, make sure to contact your doctor about it, as your health is always the top priority.