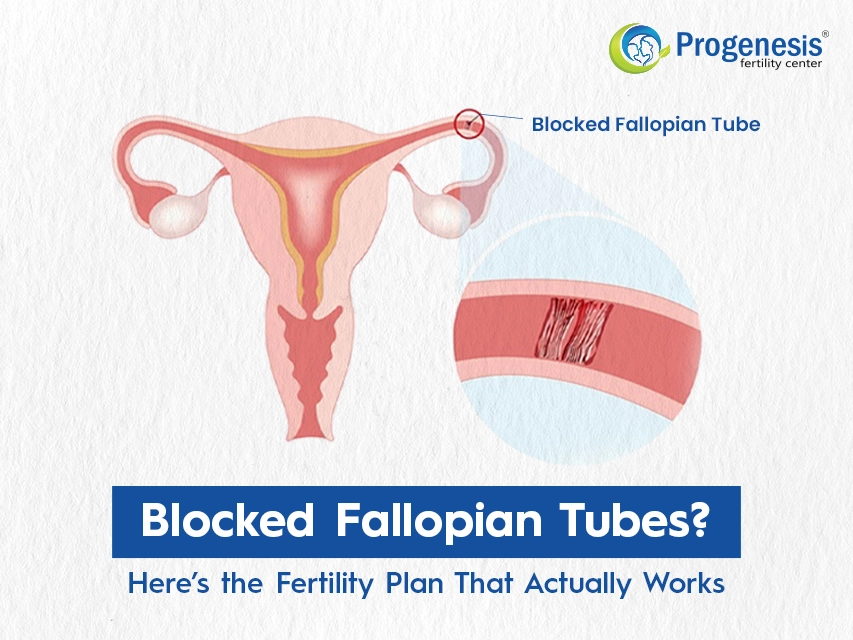
Understanding Tubal Blockage and Its Impact on Fertility
The fallopian tubes are female reproductive organs that connect the ovaries and uterus. Every month, during ovulation, which occurs around the middle of a menstrual cycle, the fallopian tubes transport an egg from the ovary to the uterus. Conception also occurs in the fallopian tube. If an egg is fertilised with sperm, it travels via the tube to the uterus for implantation.
A blocked fallopian tube prevents sperm from reaching the eggs and the fertilised egg from retuing to the uterus. Scar tissue, infection, and pelvic adhesions are among the most common causes of blocked fallopian tubes.
Effect on Fertility
Blocked fallopian tubes are a common cause of infertility. The fallopian tube is where sperm and egg meet to fertilise. A blocked tube can prevent that from happening.
If both tubes are completely blocked, pregnancy is impossible without treatment. If your fallopian tubes are partially blocked, you may become pregnant. However, the chance of ectopic pregnancy rises. This is because a fertilised egg has a more difficult time passing past a barrier to reach the uterus.
If only one fallopian tube is blocked, the blockage is unlikely to hinder fertility because an egg can still pass through the unaffected tube. Fertility medications can improve your odds of ovulating on the open side.
Diagnosing Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is a type of X-ray that examines the inside of the fallopian tubes in order to detect blockages. During HSG, your doctor will insert a dye into your uterus and fallopian tubes.
The dye allows your doctor to see more of the inside of your fallopian tubes on an X-ray. An HSG can usually be performed at your doctor's office. It is expected to happen during the initial half of your menstrual cycle. Side effects are uncommon; however, false positive results are possible.
If the HSG does not provide a firm diagnosis, your doctor may proceed with Sonohysterography that visualises the uterus and fallopian tubes using ultrasonography or laparoscopy which involves inserting a laparoscope, a thin, illuminated tube with a camera, through small incisions in the abdomen to visualize the blockage. If the doctor discovers a blockage during these procedures, he or she may attempt to remove it.
Also Read: How Can I Get Pregnant with Blocked Fallopian Tubes?
Non‑Surgical Treatment Options
There are two non-surgical ways to treat blocked fallopian tubes:
Fallopian tube recanalization: FTR is a minimally invasive procedure with a high success rate for opening up blocked tubes. The treatment also makes it possible for natural conception to happen. The process uses imaging guidance via a catheter to remove blockages in the fallopian tubes.
Hydrotubation: Hydrotubation is utilized in cases of mild obstructions in the fallopian tube that are caused by mucus. The minor obstructions are removed by flushing the tubes with fluid and medicines. This process might not be suitable for serious blockages.
Surgical Repair Procedures (Tuboplasty, Tubal Cannulation, Fimbrioplasty, Salpingostomy, Salpingectomy)
Surgical procedures to repair blocked fallopian tubes include:
Tuboplasty: Tuboplasty is a surgical technique that aims to restore the function of a woman's fallopian tubes and improve her fertility.
Tubal Cannulation: Tubal cannulation involves placing a catheter with a balloon connected to the end into the fallopian tubes. This treatment is usually used when the blockage is near the uterus.
Fimbrioplasty: The goal of fimbrioplasty is to unblock the blocked fallopian tube and restore proper functioning of the fimbriae to allow effective capturing and transfer of the oocyte.
Salpingostomy: Salpingostomy (also known as neosalpingostomy) is a technique that creates an entrance into the fallopian tube without removing the tube itself.
Salpingectomy: Salpingectomy is the surgical removal of the fallopian tube.
Also Check: Laparoscopy Surgery for Infertility & Blocked Fallopian Tubes
IVF: When to Bypass the Tubes
When fallopian tubes get blocked due to hydrosalpinx (fluid-filled, congested tubes) or extensive scarring, in vitro fertilisation (IVF) is often advised. IVF completely bypasses the fallopian tubes, allowing for laboratory fertilisation and then direct embryo transfer into the uterus.
When to bypass the tubes?
Hydrosalpinx: It is a disorder in which a fallopian tube is blocked and filled with fluid. It can significantly lower IVF success rates as the fluid may seep into the uterus and potentially harm or wash away the embryos. As a result, surgical removal of the blocked tube is often required before IVF.
Severe Scarring: Sometimes a past infection, surgery, or endometriosis may cause scarring and block the fallopian tubes which come in the way of natural pregnancy. IVF provides a way to avoid these blocked tubes in order to achieve pregnancy successfully.
Failed Tubal Ligation Reversal: If a tubal ligation (tying or clipping the tubes) fails, or if the woman wishes to have IVF, the fallopian tubes are bypassed.
Other Tubal Factors: Other tubal challenges, such as distal tubal occlusion (blockage at the end of the tube near the ovary), may require IVF to achieve pregnancy.
Also Read: Why is HSG test necessary for female infertility?
Alteative ART Options
Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT): In ZIFT, the fertilised egg or zygote is placed into the fallopian tubes rather than the uterus. ZIFT is frequently used when there are fallopian tube obstructions or other problems that make standard IVF ineffective.
Gestational surrogacy: Gestational surrogacy is the process of having another woman carry a pregnancy for someone else. Following IVF, the embryo will be put into the surrogate uterus. She will not be genetically connected to the child because the egg and sperm come from the parents or other donors. Surrogacy can only be performed in India on a non-commercial basis.
Lifestyle and Supportive Measures
Lifestyle changes and support measures that help prevent blocked fallopian tubes include:
Diet: Consuming a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids helps reduce inflammation and improve reproductive health.
Drinking water: Staying properly hydrated is necessary for maintaining a healthy cervical mucus and general body processes.
Exercise: Regular, moderate exercise improves blood supply to reproductive organs and helps maintain a healthy weight.
Quitting smoking and alcohol: These substances can harm fertility and treatment outcomes. Stress management: Techniques, including yoga, meditation, and mindfulness, may relieve stress, which is a major contributor to infertility.
Also Read: Does Alcohol and Smoking Harm Men's Fertility & Sex Life?