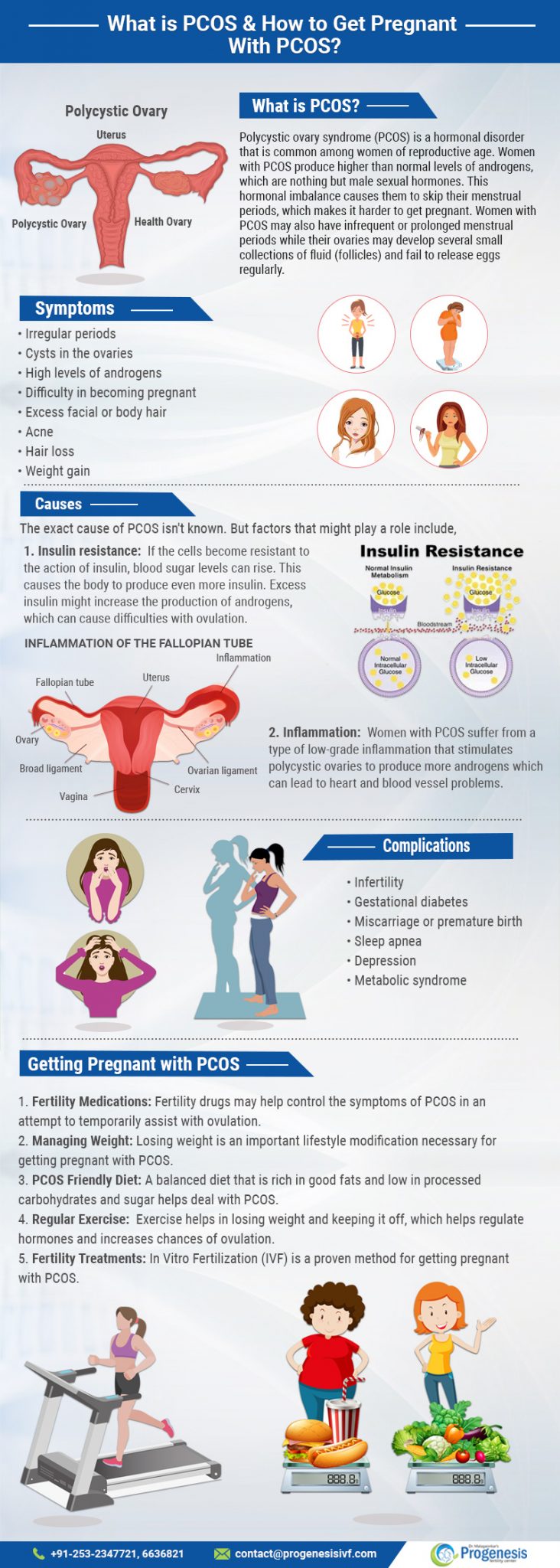
Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is a common hormonal disorder that affects millions of reproductive age women. The condition is characterized by an excess production of androgens in the female body. Androgens are a group of hormones that play an important role in male reproductive activity and other masculine traits. The abnormal production of androgens disturbs the menstrual cycle, which ultimately causes women with PCOS to have irregular or even absent periods. This makes it difficult to get pregnant. Other symptoms of PCOS include ovarian cysts, excess facial and body hair, hair loss, acne, and weight gain.
While the exact cause of PCOS remains unknown, there are factors that might be linked to the condition’s prevalence among reproductive-age women. For instance, insulin resistance causes the body to produce higher than normal levels of insulin to deal with excess blood sugar. Excess insulin production might lead to excess androgen production as well, which subsequently causes ovulation difficulties and PCOS. It has also been observed that women with PCOS exhibit a kind of low-grade inflammation that pushes the ovaries into producing more androgens. Women suffering from PCOS are also susceptible to several other complications like gestational diabetes, miscarriage or premature birth, sleep apnea, depression and metabolic syndrome.
The treatment of PCOS involves contraceptive medications, weight loss, eating a PCOS diet, regular exercise and fertility treatments like IVF. Contraceptive medications are known to control the symptoms of PCOS which helps with regularizing ovulation. A PCOS diet is rich in protein and fiber and low in carbs as the aim is to shed excess weight and restore health in combination with regular exercise. If pregnancy is still not achieved by following these measures, women with PCOS can turn to fertility treatments like IVF to realize their dream of conceiving a child of their own.